What is Nipah Virus? Check For Symptoms, Risks, And How To Stay Safe | Health News
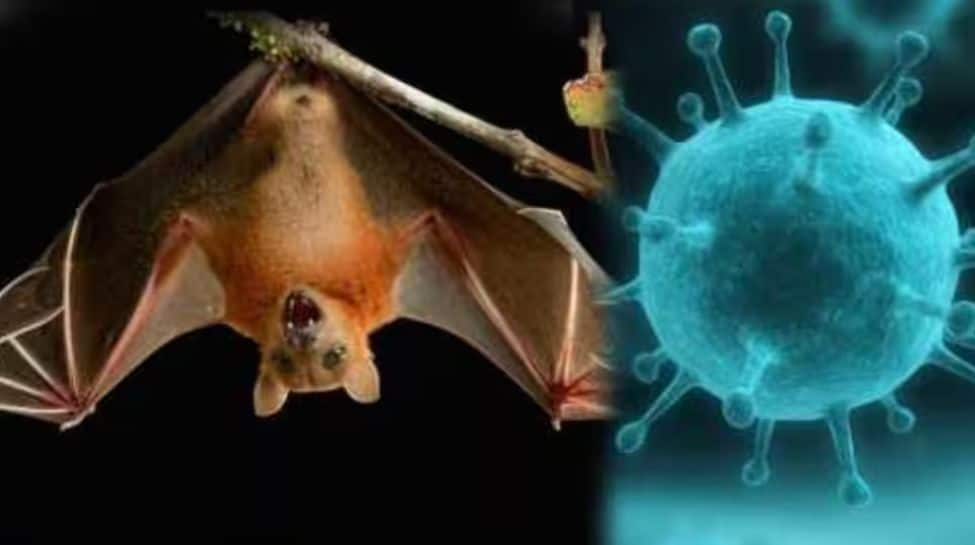
The Nipah virus (NiV) is a highly contagious and potentially deadly virus that causes severe respiratory illness and encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) in humans and animals. It was first identified in 1998–99 during an outbreak in Malaysia and Singapore, primarily affecting pig farmers. Since then, it has caused several outbreaks, particularly in South and Southeast Asia, including India and Bangladesh.
What is Nipah Virus?
Nipah virus belongs to the family Paramyxoviridae, genus Henipavirus. It is a zoonotic virus, meaning it can spread from animals to humans. The natural reservoir of the virus is the fruit bat (also called flying foxes), but it can also be transmitted through infected pigs or directly from human to human.
Once again, Kerala is grappling with the ominous reappearance of the Nipah Virus. The state’s health department has raised an alarm following two mysterious deaths in Kozhikode, suspecting Nipah Virus (NiV) as the cause.
The virus is listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a priority disease that poses a public health risk due to its epidemic potential and lack of treatment or vaccine.
How is Nipah Virus Transmitted?
Nipah can be transmitted through:
- Direct contact with infected animals (bats, pigs).
- Consumption of contaminated food (like raw date palm sap tainted by bat saliva or urine).
- Human-to-human transmission via bodily fluids, saliva, or close contact with an infected person.
Symptoms of Nipah Virus Infection
Symptoms typically appear 4 to 14 days after exposure and may include:
Early Symptoms:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Vomiting
- Sore throat
- Progressive Symptoms:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Altered consciousness
- Neurological signs of acute encephalitis
Severe Cases:
- Seizures
- Coma within 24–48 hours
- Respiratory distress
Precautions and Prevention
As there is no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment for Nipah virus yet, prevention is key. Here are important precautions to take:
1. Avoid Contact with Bats and Sick Animals
- Do not consume fruits that may have bat bite marks.
- Avoid visiting places where fruit bats are known to roost.
2. Do Not Drink Raw Date Palm Sap
- Bat saliva or urine can contaminate the sap.
- Only consume boiled or processed sap.
3. Practice Good Hygiene
- Wash hands regularly with soap and water.
- Avoid contact with an infected person’s body fluids, clothes, or beddings.
4. Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Health workers and caregivers should wear gloves, masks, and other PPE when handling suspected or confirmed cases.
5. Quarantine and Report Suspected Cases
- Immediate isolation of infected individuals.
- Report symptoms to health authorities without delay.
When to Seek Medical Help?
Seek medical attention immediately if you or someone close shows signs of:
- Persistent fever with neurological symptoms
- Difficulty breathing
- Sudden confusion or unconsciousness
Nipah virus is a serious public health threat with high mortality and no specific cure. However, with awareness, hygiene practices, and timely medical intervention, the spread can be controlled. Public health authorities continue to monitor for outbreaks, and research is ongoing for vaccine development. Until then, prevention and vigilance remain our best defense.
(This article is intended for your general information only. Zee News does not vouch for its accuracy or reliability.)






