Why are Andhra Pradesh and Telangana fighting over Banakacherla project?
Story so far: Andhra Pradesh and Telangana are once again embroiled in a water dispute, this time over the Banakacherla project. The ambitious project which will link the Godavari and Krishna River basins via reservoirs, canals, and lift irrigation scheme is Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister N. Chandrababu Naidu’s pet project, first envisioned in 2014 after the bifurcation of Andhra and Telangana. With Mr. Naidu again at the helm in Andhra, he seeks speedy construction of the project, but faces tough opposition from Telangana.
Also Read: Explained | The Telangana- Andhra Pradesh water dispute
“Nearly 2,000 Thousand Million Cubic Feet (tmc ft) water from the Godavari flows into the sea, while the Rayalaseema area suffers from drought,” said Andhra Pradesh Finance Minister Payyavula Keshav in February, while stressing the need for the Godavari-Banakacherla project. In response, the Telangana government has accused Andhra of violating the inter-state river water sharing agreement agreed to in the AP Reorganisation Act, 2014.
Here’s a look at the project and row between the states:
What is the Banakarchela project?
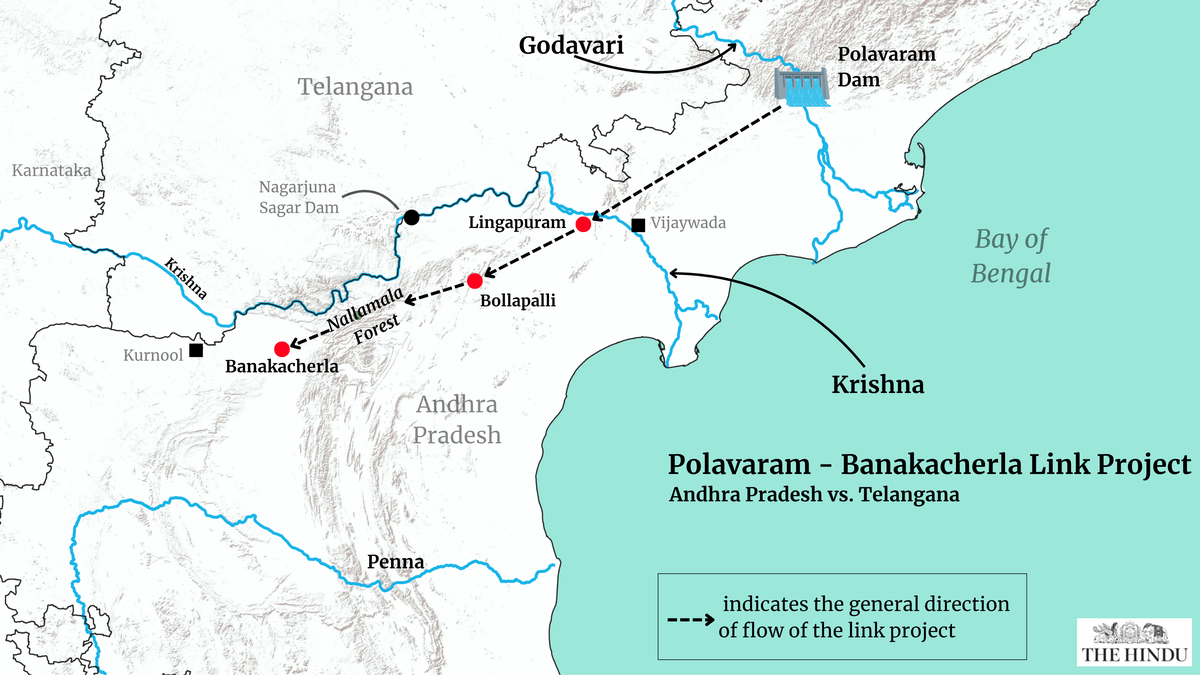
Post-bifurcation, Andhra Pradesh has strived to utilise the ‘surplus’ Godavari waters to provide relief to a drought-prone Rayalseema region. As per Mr. Naidu’s vision, by interlinking the Godavari-Krishna basins, the 2000 tmc. ft. Godavari river water flowing into the Bay of Bengal can be diverted from the Polavaram Dam towards the Banakacherla region in Rayalseema.
To link Godavari and Krishna, Andhra plans on diverting Godavari flood waters to Prakasam Barrage on Krishna river at Vijayawada and then pump it to the Bollapalli reservoir via canals, and irrigation lifts. From there, tunnels passing under Nallamala forests will transfer water to Banakacherla reservoir, benefitting Kadapa and Kurnool regions.
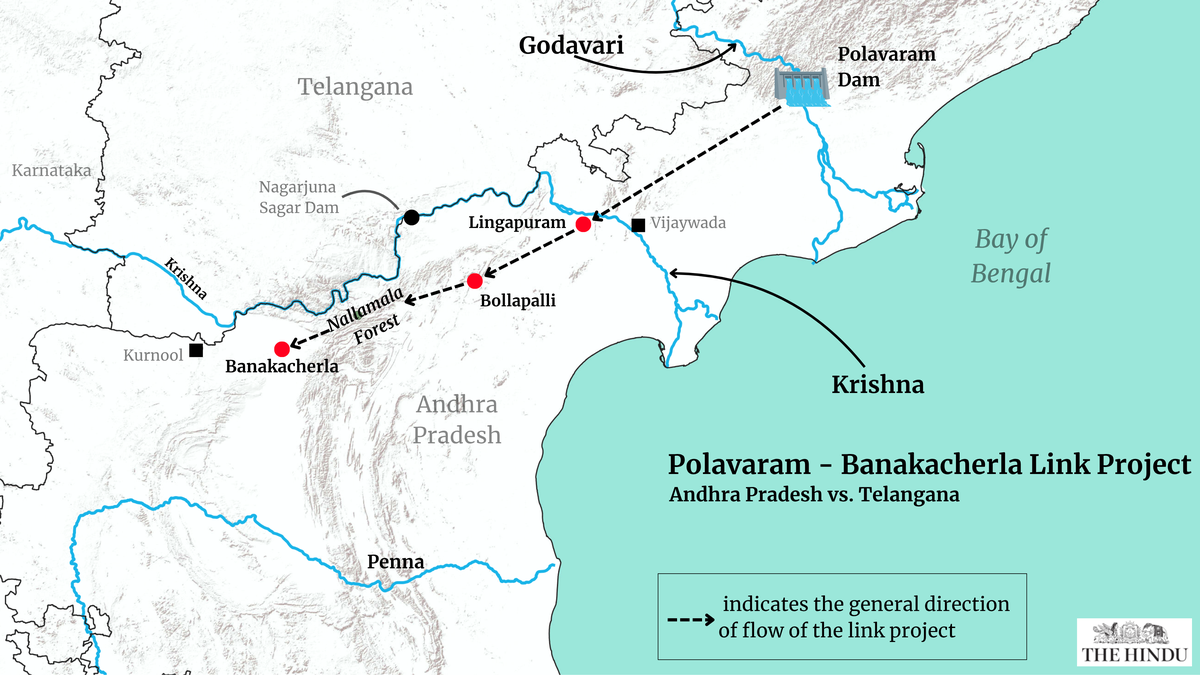
Polavaram-Banakacherla Link Project
| Photo Credit:
Gautam Doshi
With an estimated cost of ₹80,112 crore, Banakacherla project requires the acquisition of 40,500 acres including forest land.
Annually, 3000 tmc of Godavari floodwaters run into the Bay of Bengal during the 100-odd days of monsoon. Andhra wishes to divert 200 tmc of this run-off towards Krishna basin by enhancing Polavaram Right Main Canal’s capacity to 38,000 cusecs, Thatipudi Lift Irrigation Scheme’s canal to 10,000 cusecs and construct a reservoir at Bollapalli with a storage capacity of 150 tmc ft.
Powered by six lift stations at Harischandrapuram, Lingapuram, Vyyandana, Gangireddypalem, and Nakirekallu, with a total power demand over 4000 MW, water will be transfered to Banakacherla dam via tunnels under Nallamala forest. Andhra sees this as the most viable solution to Rayalseema’s drought woes.
Andhra’s argument
In 2013, the Krishna Water Disputes Tribunal, divided the available 2130 tmc ft of Krishna waters among undivided Andhra (1005 tmc), Karnataka (907 tmc) and Maharashtra (666 tmc). Since the award, both Telugu states have been crying foul as the Tribunal has robbed them of its freedom to use surplus water in its natural catchment. The Tribunal, in its calculations, has equally divided the surplus water of 285 tmc between undivided Andhra and the other two states.
Post-bifurcation, Mr. Naidu and then-Telangana CM K Chandrashekhara Rao struck deal allowing Telangana to utilise 299 tmc ft and Andhra 512 tmc ft of the 811 tmc ft of Krishna river waters, awarded to unified Andhra Pradesh by the Bachawat Tribunal in 1976.
Similarly, the Godavari Water Dispute Tribunal (GWDT) ordered Andhra Pradesh to divert 80 tmc ft of Godavari waters from Polavaram to Krishna river to be shared upstream with Karnataka and Maharashtra. Without any mention of surplus waters, the tribunal allotted 1486 tmc ft to undivided Andhra.
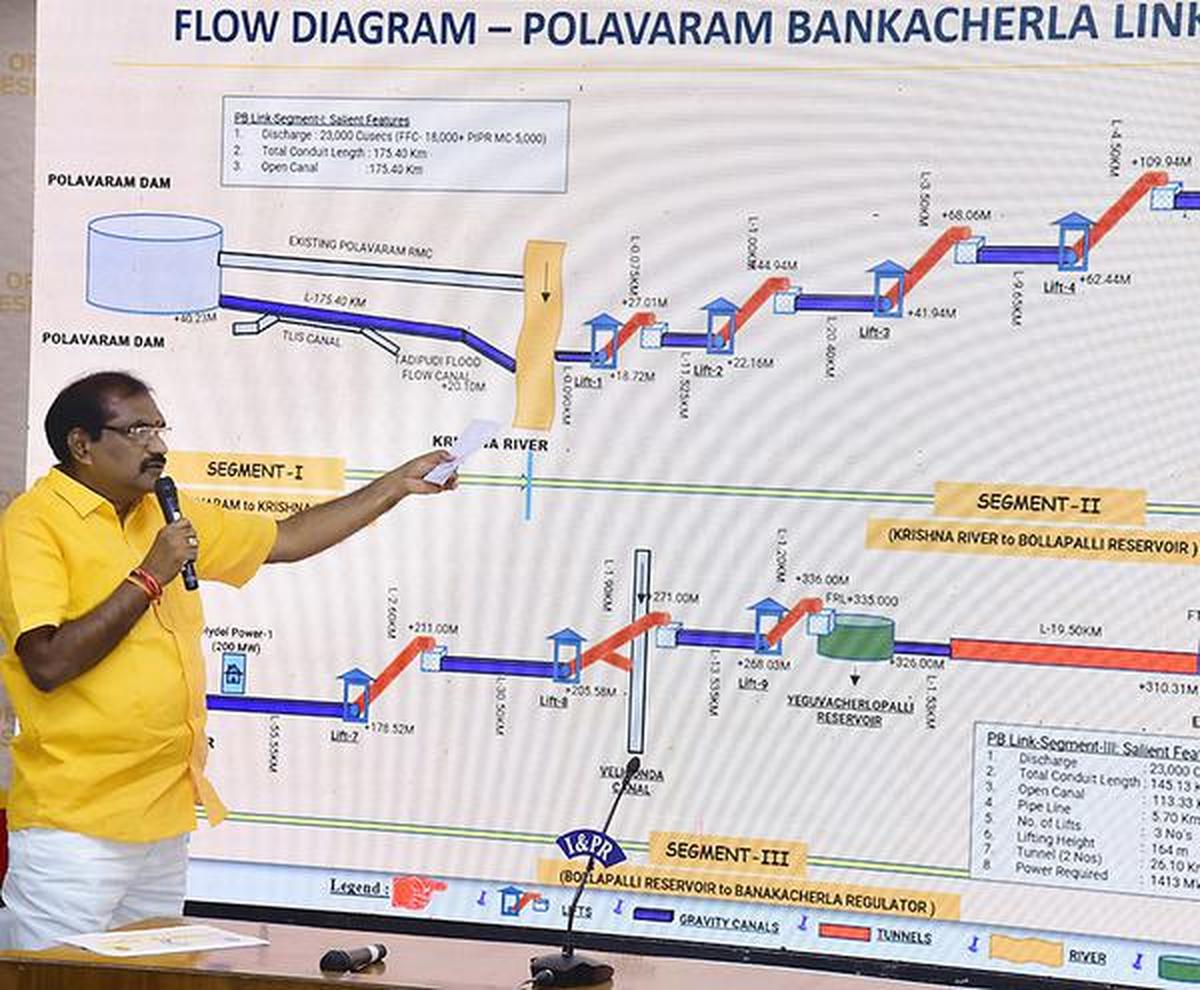
Andhra Pradesh Water Resources Minister Nimmala Ramanaidu explaining the Banakacherla project at a press meet.
| Photo Credit:
The Hindu
Hence, the Andhra Pradesh government claims that with the Polavaram-Banakacherla link, the State was only using ‘unused surplus waters’ flowing into Andhra Pradesh after the needs of the upper riparian States are met.
Affirming that both Polavaram project and Banakacherla were in compliance with the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014, Andhra has requested to maintain status quo on the allocations of the Krishna river water made by the Tribunal. Mr. Naidu has also asked Telangana to discuss with the Centre about the legal sanctity to utilise flood waters flowing into the sea.
Telangana’s argument
On the other hand, Telangana has claimed that the project violates the AP Reorganisation Act, 2014 as the upper riparian state was allotted 968 tmc ft of Godavari waters while Andhra was given 500 tmc ft by GWDT. Telangana Chief Minister Revanth Reddy claims that as the Tribunal did not mention allocation of ‘surplus waters’, Banakacherla was a threat to the state’s water security. Telangana’s irrigation minister N. Uttam Kumar Reddy accuses Andhra and the Godavari River Management Board (GRMB) of hiding the project details. He claims that Andhra was proceeding with the project without getting any clearances from the statutory agencies or doing a thorough impact study.
What do experts say?
“Increasing the Polavaram canal capacity will significantly alter the natural west-to-east flow regime. This could reduce freshwater inflows to downstream deltas, leading to increased salinity intrusion, loss of sediment and nutrients, disruption of aquatic ecosystems, and harm to agriculture and fisheries in the Godavari and Krishna deltas,” explains Shrinivas Badiger, a Fellow at Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and Environment.
Elaborating on the Polavaram canal enhancement, Shripad Dharmadhikary, founder of water research organisation Manthan, says, “It will impact the delta/ estuary downstream of the Polavaram project. Reduced flow will bring down the sediments and silt flowing downstream, reducing soil fertility, increasing saltwater ingress , thus impacting productivity of agriculture, fish and nearby mangroves”.
Countering Andhra’s assertion that the project was the ‘only solution’ to Rayalseema’s water woes, Mr. Badiger says, “Other measures like groundwater recharge, rainwater harvesting, micro-irrigation, and smaller intra-basin transfers have not been fully exhausted. The project also faces significant legal, environmental, and interstate challenges that complicate its implementation”.
Effects of the tunneling through the Nallamala forests would be severe, warn experts. “Disrupting soil stability and groundwater flow will affect critical wildlife habitats. It will also threaten endangered species, including tigers and elephants, and risks damaging the ecological balance of this protected forest area. It may also affect indigenous communities dependent on the forest,” adds Mr. Badiger.

What is the current state of the project?
On June 30, the Central Environmental Expert Committee (EAC) refused to grant environmental clearance to the proposed Polavaram–Banakacherla Link Project. Citing multiple objections, it stated that any progress must be in line with the 1980 verdict of the GWDT. Moreover, it urged Andhra to consult the Central Water Commission (CWC) for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), Terms of Reference (ToR), floodwater evaluation and inter-State water-sharing concerns. Andhra’s proposal has now been returned to the state for further clarification and revision.
Published – July 04, 2025 04:02 pm IST







